Title: Troubleshooting: Definition, Types and How it Works
For You. Get More Information from our site @iwanrj.com free.
Have you ever experienced problems with network, software, hardware, or other computer-related components? This is indeed quite troublesome and can interfere with work productivity. Of the many alternatives, troubleshooting is one approach you can take to solve the problem.
Troubleshooting has different types and methods depending on the source of the problem. Troubleshooting will identify, evaluate, and review the source of errors on computer devices. Therefore, this activity should not be done haphazardly.
Definition of Troubleshooting
According to TechTarget, troubleshooting is a systematic approach to find and solve problems. The constraints or problems referred to are usually complex, for example errors in computer equipment, networks, software systems, and so on. Troubleshooting activities aim to ensure that the system can operate normally again.
When troubleshooting, a computer technician will usually adopt a problem isolation approach. The approach is carried out by collecting information related to the constraints that occur. Call it like reduced functionality of a component or unwanted behavior.
Based on the information that has been collected, the technician will remove or eliminate a number of components that are suspected of causing the error. The goal is to determine whether the problem still exists or has disappeared. In addition, this step is also useful for identifying component incompatibility problems.
The troubleshooting methodology is basically finding the general cause of a problem and isolating it so that it can be examined. That way, technicians can diagnose problems and implement clear solutions.
Troubleshooting type
Technically, there are two types of troubleshooting that you need to know about, namely forward and backward. Here’s an explanation:
1. Troubleshooting forward
As the name implies, forward troubleshooting is a technique used to detect problems from the start of the computer assembly. This type of troubleshooting is usually used by people who are used to assembling computers. Checks are carried out before the computer is turned on or given electricity. For example, checking the power supply and power socket, installing RAM, and so on.
2. Troubleshooting backwards
Troubleshooting backwards is a technique used to detect problems on the computer after it is turned on. This technique is widely used because problems appear more often after the device is turned on. For example, the floppy disk cannot be read, the CPU button does not work, and so on.
The types of troubleshooting are based on the cause of the problem. Among them are as follows:
- Bad usage habits
Bad habits of users can reduce the performance and performance of the device. Examples include opening multiple applications at the same time or using an overclocked device. The troubleshooting effort to overcome this is to restart or leave the computer turned off for 10 to 20 minutes.
- Poor design factor
As a user, you certainly feel uncomfortable if the computer you are using is poorly designed. For example port placement is unusual and careless, where this has the potential to cause cable and USB installation errors. Error entering the port will be detected by the computer and raises a warning in the form of a dialog box.
- Accidental error
Users may accidentally make mistakes that affect system performance. For example pressing many keyboard keys together so that the cursor cannot move. The troubleshooting effort for this problem is by restarting.
- Poor system quality
Constraints can also occur as a result of poor quality of the system itself. Each product has its own advantages and disadvantages, so the problems that occur vary depending on the system. To solve the problem, you should follow the default manual from the brand in question.
How Troubleshooting Works
1. Gather information
The first way troubleshooting works is to collect all information related to the problem. This information can contain the loss of the ability of certain components or unwanted changes occur. This step aims to identify obstacles as well as understand how to overcome them.
2. Describe the problem
Comprehensively describing the problem will help the troubleshooter find the root of the problem. There are several things that must be considered, such as symptoms, time, components, and conditions when an error occurs. This will reveal which components are still safe and experiencing problems.
3. Determine the cause of the problem
At this stage, troubleshooters generally use a split-half approach or isolate the problem through a process of elimination. This method is especially effective when the device has a system with a number of parts in series. Each part will be tested individually until the source of the problem is found.
4. Create and test the solution
After the root of the problem has been found, the next step is to create and develop a plan to overcome the problem. The hypotheses or plans made are then tested until a solution is identified. If all else fails, troubleshooting must be repeated from the previous stage.
5. Implement the solution
When a problem is understood and identified, the next step is implementing a solution. At this stage, the troubleshooter must repair, adjust, or even replace the component causing the problem. Retesting is also needed to ensure that the problem has actually been fixed.
6. Analyze the results
Sometimes, a solution even creates new problems in other components. Analysis of troubleshooting results is a form of anticipation of the potential for new problems to occur. Therefore, the troubleshooter must monitor and ensure changes made do not affect the performance of the system or other connected components.
7. Documenting the process
Documenting the troubleshooting process is the final step that can be taken. Even though it technically has nothing to do with the repair process, it will help other troubleshooters when they encounter similar problems.
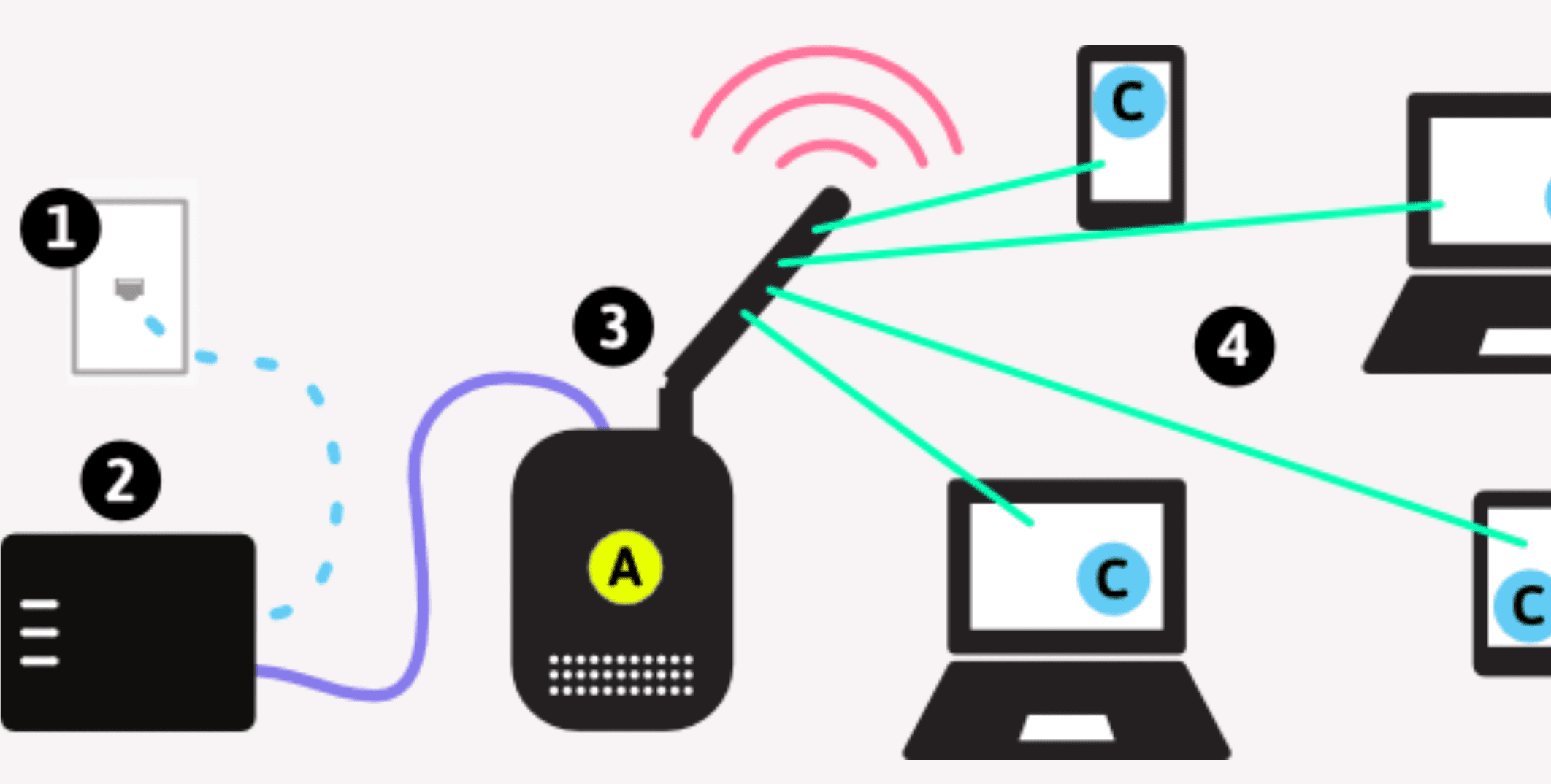
Network Troubleshooting Steps
1. There is an exclamation mark
- “
2. There is a problem with the laptop’s Wi-Fi card
3. Restart the modem
4. There is a netcut user attack
Netcut is software that cuts the internet connection when connected to a public network, such as a hotspot network. So your connection can be lost at any time, the cause is from the netcut application used by other users.
To overcome this you can change your IP and use protective software, such as anti-netcut or anti-ARP. In this way, the cause of the computer’s Wi-Fi not being connected can be handled properly.